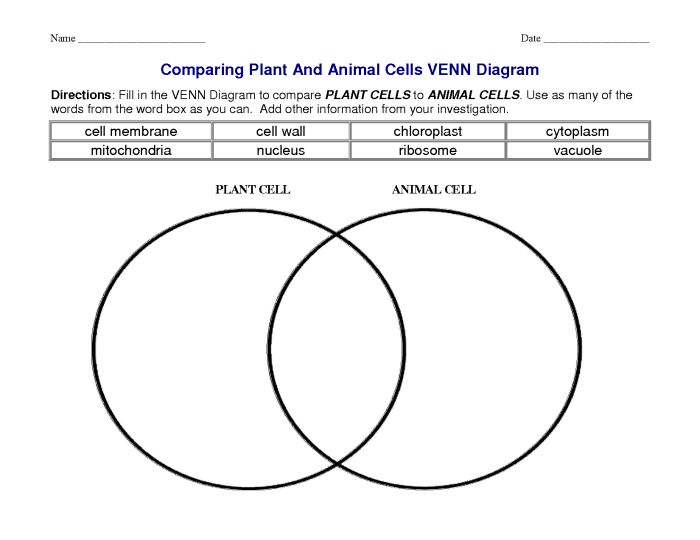
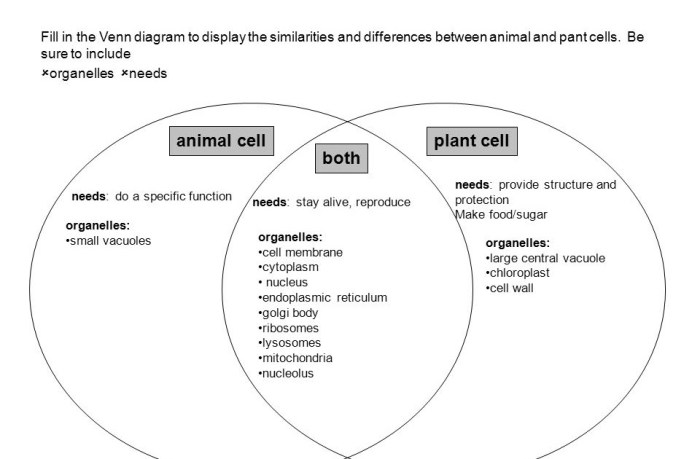
Comparing plant and animal cells venn diagram – The comparative analysis of plant and animal cells, encapsulated within a comprehensive Venn diagram, unveils a fascinating realm of cellular diversity. This in-depth exploration delves into the structural intricacies, functional specializations, and evolutionary distinctions that shape these fundamental units of life.
Through a meticulous examination of their unique organelles, cell walls, and membranes, we uncover the remarkable adaptations that enable plants and animals to thrive in their respective environments. Moreover, by contrasting the processes of cell division, energy production, movement, and communication, we gain a profound understanding of the fundamental principles that govern cellular life.
Cell Structures
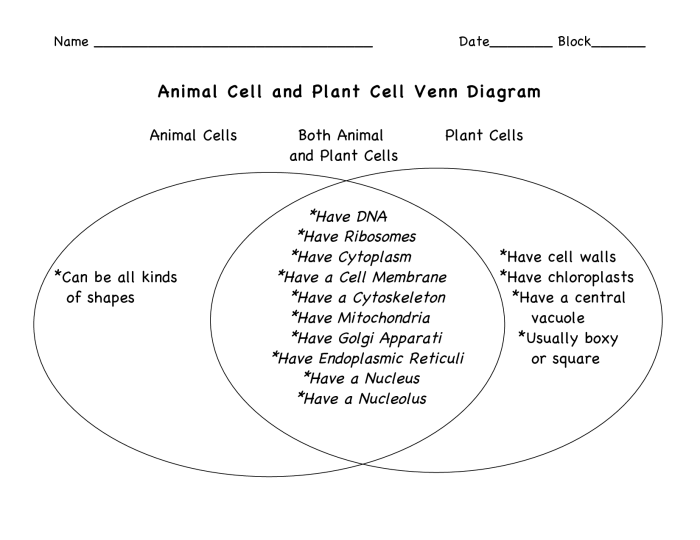
Plant and animal cells exhibit distinct structural differences. Plant cells possess a rigid cell wall composed of cellulose, which provides structural support and protection. Animal cells, on the other hand, lack a cell wall but have a flexible plasma membrane that regulates the passage of substances.
Furthermore, plant cells contain chloroplasts, organelles responsible for photosynthesis, the process by which light energy is converted into chemical energy. Animal cells lack chloroplasts but possess mitochondria, organelles that generate energy through cellular respiration.
Cell Wall and Membranes
The cell wall of plant cells provides rigidity and protection, enabling them to withstand changes in osmotic pressure. It also facilitates cell-to-cell adhesion and provides a framework for cell growth and development.
Animal cell membranes, composed primarily of phospholipids, regulate the passage of substances into and out of the cell. They maintain the cell’s shape and protect it from external influences.
Cell Division
Cell division is crucial for growth, development, and reproduction. Plant cells undergo mitosis, a process that results in two identical daughter cells. Animal cells, however, can undergo both mitosis and meiosis.
Mitosis produces two identical daughter cells, each with the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell. Meiosis, on the other hand, is a specialized form of cell division that produces four daughter cells with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell.
This process is essential for sexual reproduction.
Energy Production
Plant cells utilize chloroplasts to convert light energy into chemical energy through photosynthesis. The energy stored in glucose molecules is then used to fuel cellular processes.
Animal cells rely on mitochondria for energy production. Mitochondria carry out cellular respiration, a process that breaks down glucose molecules to generate ATP, the primary energy currency of the cell.
Cell Movement and Communication, Comparing plant and animal cells venn diagram
Plant cells lack the ability to move independently, but they can exhibit tropisms, directional growth responses to external stimuli such as light or gravity.
Animal cells, on the other hand, possess specialized structures for movement, such as cilia and flagella. Cell signaling and communication are also essential for coordinating cell activities in both plant and animal cells.
Query Resolution: Comparing Plant And Animal Cells Venn Diagram
What are the key differences between plant and animal cells?
Plant cells possess a rigid cell wall, chloroplasts for photosynthesis, and a large central vacuole, while animal cells lack these structures and have a flexible cell membrane.
How does cell division differ in plant and animal cells?
Plant cells undergo cytokinesis by forming a cell plate, while animal cells use a cleavage furrow.
What is the role of mitochondria in both plant and animal cells?
Mitochondria are responsible for cellular respiration, generating energy for the cell.