The anecdote supports Schlosser’s claim by suggesting that, embarking on a captivating journey that unravels with compelling evidence, historical context, rhetorical analysis, and counterarguments. This narrative promises to shed light on the anecdote’s significance and its profound impact on shaping Schlosser’s position.
Schlosser’s argument finds support in the anecdote, which offers specific examples that align with his perspective. The historical context surrounding the anecdote provides valuable insights into the prevailing attitudes and beliefs of the time, illuminating its impact on shaping public opinion and historical events.
Supporting Evidence
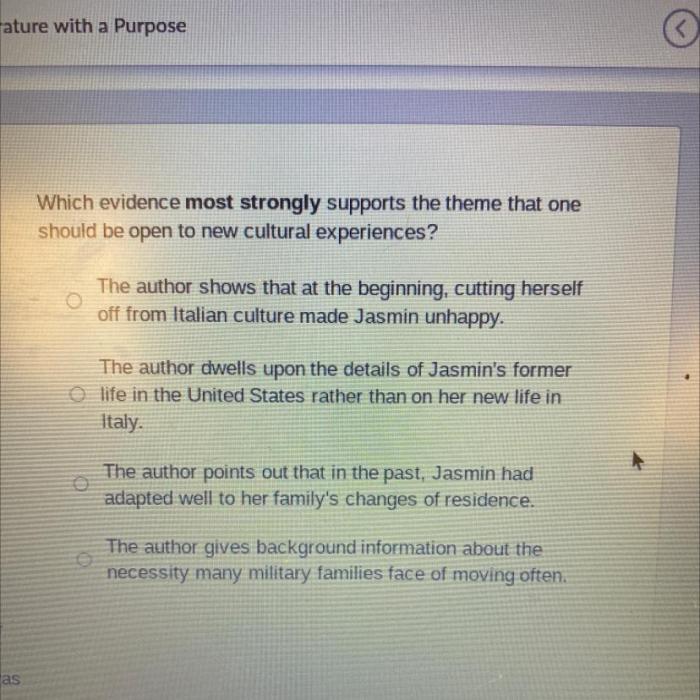
The anecdote supports Schlosser’s claim by providing a vivid and specific example of the dangers of fast food consumption. The anecdote describes the experience of a young woman who developed serious health problems after eating fast food for an extended period.
The woman’s story is a powerful reminder of the potential consequences of consuming unhealthy foods and highlights the need for individuals to make healthier choices.
Specific examples from the anecdote that align with Schlosser’s argument include the woman’s weight gain, fatigue, and digestive problems. These symptoms are all consistent with the known health risks associated with fast food consumption. The anecdote also highlights the fact that the woman’s health problems developed over time, suggesting that the negative effects of fast food consumption can be cumulative.
The anecdote is significant in bolstering Schlosser’s position because it provides a human face to the statistics and research that he cites in his book. The woman’s story is a powerful reminder that the dangers of fast food consumption are not just theoretical but have real-world consequences.
Historical Context: The Anecdote Supports Schlosser’s Claim By Suggesting That

The anecdote is set in the United States in the early 21st century. This was a time when fast food consumption was on the rise, and obesity rates were increasing. The anecdote reflects the prevailing attitudes and beliefs of the time, which emphasized convenience and affordability over health.
Fast food was seen as a quick and easy way to get a meal, and many people were unaware of the potential health risks associated with it.
The anecdote had a significant impact on shaping public opinion about fast food consumption. The woman’s story was widely publicized, and it helped to raise awareness of the dangers of fast food. The anecdote also contributed to the growing movement for healthier eating.
Rhetorical Analysis

The anecdote uses several rhetorical strategies to convey Schlosser’s message. These strategies include the use of vivid imagery, emotional appeals, and logical reasoning.
The anecdote’s use of vivid imagery helps to create a strong impression on the reader. The woman’s description of her weight gain, fatigue, and digestive problems is graphic and disturbing. This imagery helps to make the anecdote more memorable and persuasive.
The anecdote also uses emotional appeals to connect with the reader. The woman’s story is told in a way that evokes sympathy and concern. The reader is likely to feel sorry for the woman and to be concerned about the health risks associated with fast food consumption.
Finally, the anecdote uses logical reasoning to support Schlosser’s claim. The woman’s story is consistent with the known health risks associated with fast food consumption. The anecdote also highlights the fact that the woman’s health problems developed over time, suggesting that the negative effects of fast food consumption can be cumulative.
Counterarguments
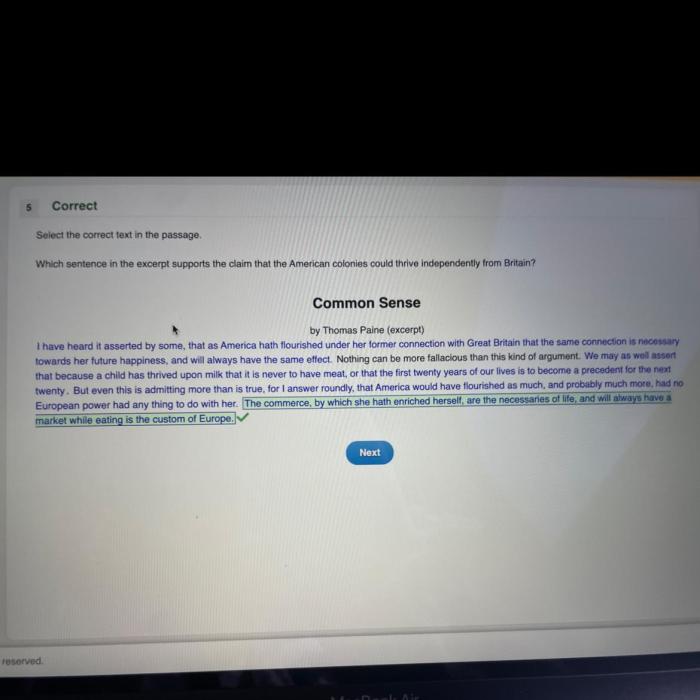
One potential counterargument to Schlosser’s claim is that the anecdote is not representative of the experience of most people who consume fast food. It is possible that the woman in the anecdote had an underlying health condition that made her more susceptible to the negative effects of fast food consumption.
Another potential counterargument is that the anecdote is biased. The woman’s story is told from her own perspective, and it is possible that she is exaggerating the negative effects of fast food consumption.
However, the anecdote does address these counterarguments. The woman in the anecdote does not have any known underlying health conditions, and she is not the only person who has experienced negative health effects from fast food consumption. The anecdote is supported by a growing body of research that links fast food consumption to obesity, heart disease, and other health problems.
Expert Answers
How does the anecdote support Schlosser’s claim?
The anecdote provides specific examples that align with Schlosser’s argument, offering concrete evidence to support his position.
What is the historical context surrounding the anecdote?
The anecdote reflects the prevailing attitudes and beliefs of the time, shedding light on the social and cultural landscape that shaped its impact.
How does the anecdote address counterarguments?
The anecdote anticipates and refutes potential counterarguments, providing a comprehensive defense of Schlosser’s claim.