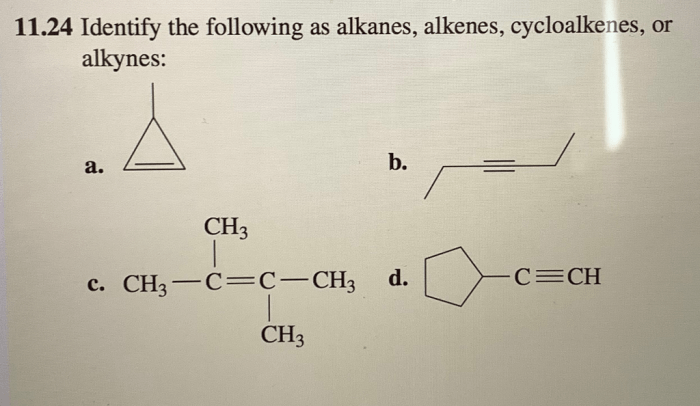
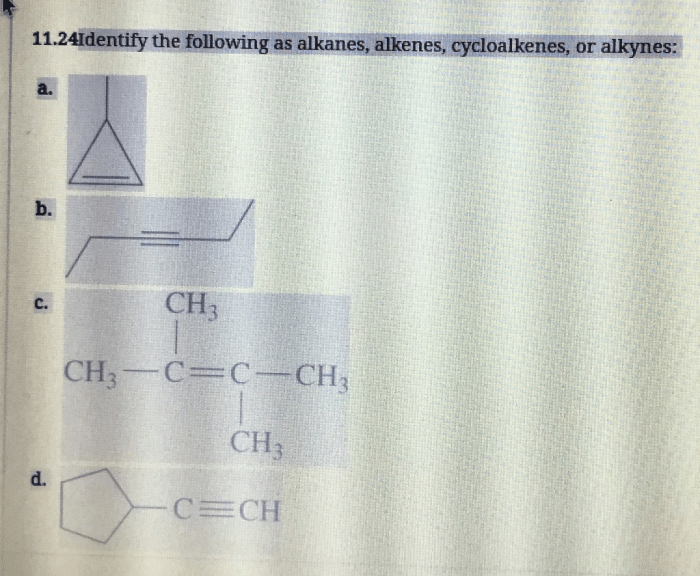
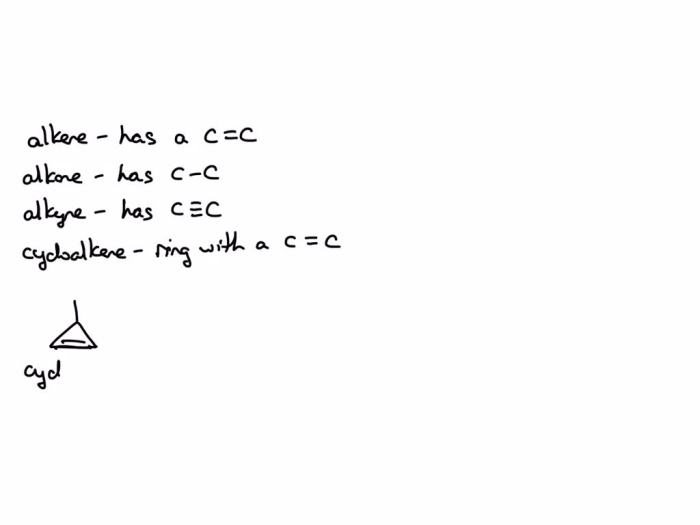Identify the following as alkanes alkenes cycloalkenes or alkynes – In the realm of organic chemistry, hydrocarbons reign supreme, and among them, alkanes, alkenes, cycloalkenes, and alkynes stand out as distinct classes. Embark on a captivating journey to unravel the intricacies of these compounds, their structural nuances, and their unique properties.
This comprehensive guide will empower you to identify these hydrocarbons with precision, unlocking a deeper understanding of their behavior and significance in the chemical world.
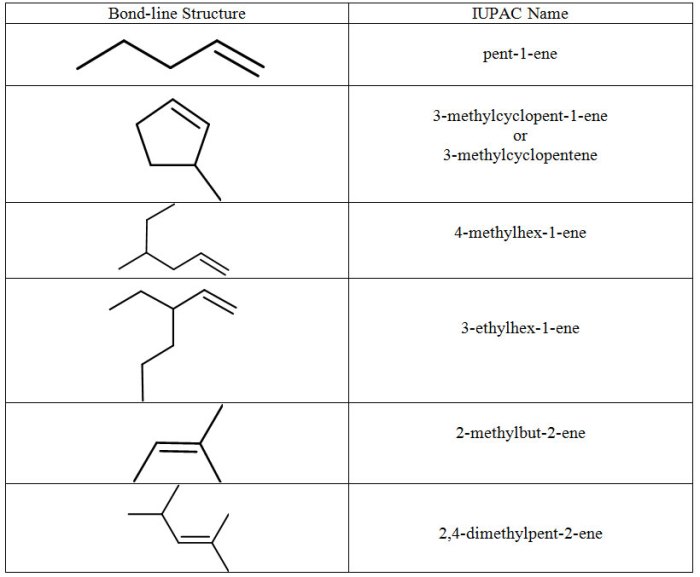
Identifying Alkanes, Alkenes, Cycloalkenes, and Alkynes
Hydrocarbons are organic compounds composed of carbon and hydrogen atoms. They can be classified into four main types based on their structure and bonding: alkanes, alkenes, cycloalkenes, and alkynes.
Identifying Alkanes
- Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons, meaning they have only single bonds between carbon atoms.
- They have the general formula CnH2n+2.
- Examples of alkanes include methane (CH4), ethane (C2H6), and propane (C3H8).
- Alkanes are nonpolar and have low reactivity.
Identifying Alkenes
- Alkenes are unsaturated hydrocarbons, meaning they have at least one double bond between carbon atoms.
- They have the general formula CnH2n.
- Examples of alkenes include ethene (C2H4), propene (C3H6), and butene (C4H8).
- Alkenes are more reactive than alkanes due to the presence of the double bond.
Identifying Cycloalkenes
- Cycloalkenes are unsaturated hydrocarbons that contain a ring of carbon atoms with at least one double bond.
- They have the general formula CnH2n-2.
- Examples of cycloalkenes include cyclopentene (C5H8) and cyclohexene (C6H10).
- Cycloalkenes are more reactive than alkanes but less reactive than alkenes.
Identifying Alkynes, Identify the following as alkanes alkenes cycloalkenes or alkynes
- Alkynes are unsaturated hydrocarbons that have at least one triple bond between carbon atoms.
- They have the general formula CnH2n-2.
- Examples of alkynes include ethyne (C2H2), propyne (C3H4), and butyne (C4H6).
- Alkynes are the most reactive of the four types of hydrocarbons due to the presence of the triple bond.
| Property | Alkanes | Alkenes | Cycloalkenes | Alkynes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Structural Formula | CnH2n+2 | CnH2n | CnH2n-2 | CnH2n-2 |
| Hybridization | sp3 | sp2 | sp2 | sp |
| Bond Angles | 109.5° | 120° | 120° | 180° |
| Reactivity | Low | Moderate | Moderate | High |
FAQs: Identify The Following As Alkanes Alkenes Cycloalkenes Or Alkynes
What is the key difference between alkanes and alkenes?
Alkanes possess only single bonds between carbon atoms, resulting in a saturated structure, while alkenes contain at least one carbon-carbon double bond, introducing unsaturation into their molecular framework.
How can I identify a cycloalkene based on its structural formula?
Cycloalkenes exhibit a ring structure with alternating single and double bonds between carbon atoms, forming a closed loop.
What is the hybridization of the carbon atoms in an alkyne?
The carbon atoms involved in the triple bond of an alkyne are sp-hybridized, resulting in a linear molecular geometry.